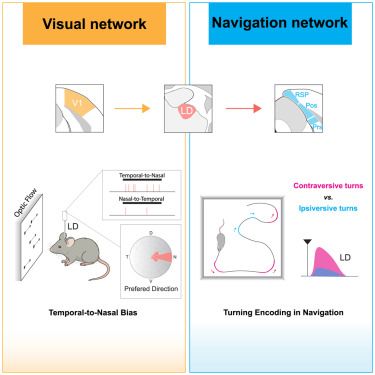
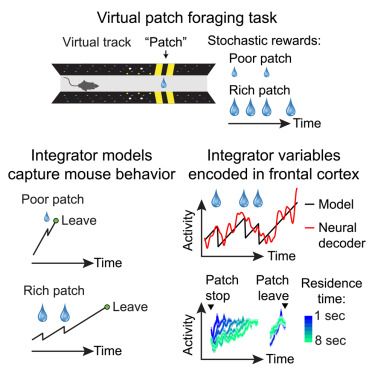
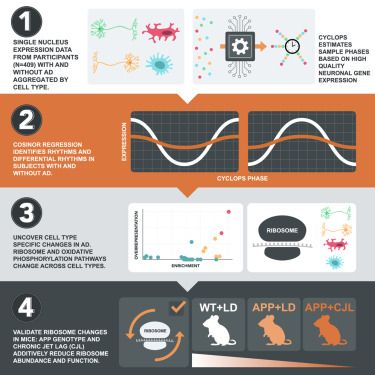
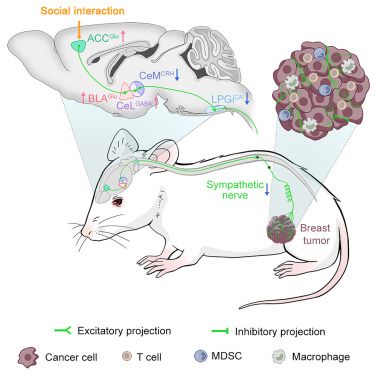
Online now:
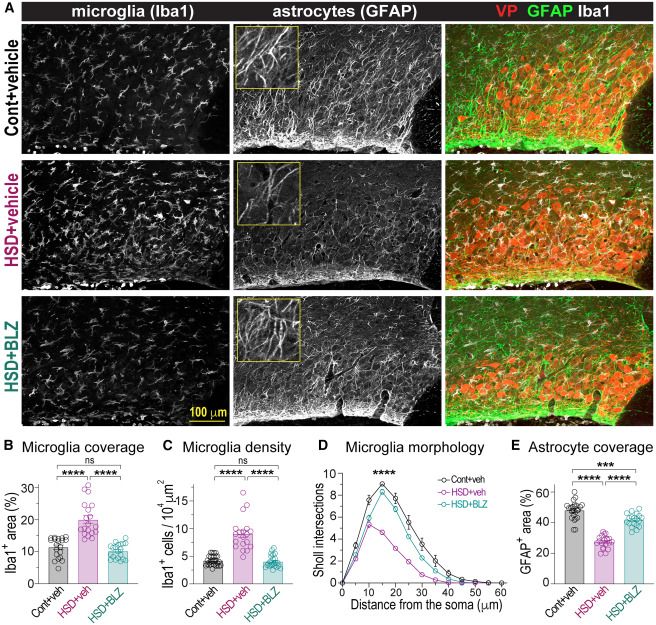
Microglia regulate neuronal activity via structural remodeling of astrocytes
Gu et al. showed that in rats fed a high-salt diet, reactive microglia accumulate around vasopressin-secreting neurons, phagocytosing astrocytic elements and pruning astrocytes. This causes glutamate spillover, increased neuronal activity, and excessive vasopressin release, contributing to salt-induced hypertension. The study reveals a novel mechanism by which microglia regulate synaptic transmission and neuronal activity through structural remodeling of astrocytes in the adult brain.